World AMR Awareness Week in focus: Primary care audits
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains a critical concern, largely fuelled by inappropriate antibiotic prescribing and the unnecessary use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. In an ongoing commitment to combat this global health threat, Ecraid’s pan-European primary care research network is continuing its yearly audit focused on the management of respiratory tract infections by general practitioners.
Understanding respiratory tract infections in primary care
Now in its fifth consecutive year, the audit has become part of the EU-funded ECRAID-Base POS-ARI-PC study and seeks to uncover insights into the variations of care provided by over 150 general practitioner (GP) practices in 18 countries. The data and insights derived from these audits have proven highly successful, resulting in, amongst others, the publication of a well-received article titled ‘Point-of-care testing, antibiotic prescribing, and prescribing confidence for respiratory tract infections in primary care: a prospective audit in 18 European countries’. This publication achieved remarkable success, becoming the most-read article in BJGP Open, with over 6,300 views and downloads in 2022 alone.
Alike van der Velden, the coordinator of the primary care network and POS-ARI-PC lead, emphasises the significance of this initiative.
“When we first started, there was very little information available on antibiotic prescribing practices and the treatment approaches of general practitioners for patients with respiratory tract infections – one of the most frequently presented complaints at GP practices around Europe. Through our yearly audit, we meticulously capture details such as antibiotic prescribing, and the type of antibiotics used. This information not only provides us with cross-countries comparisons and longitudinal data, but also serves as constructive feedback for individual practices to facilitate their engagement in antimicrobial stewardship programmes.”
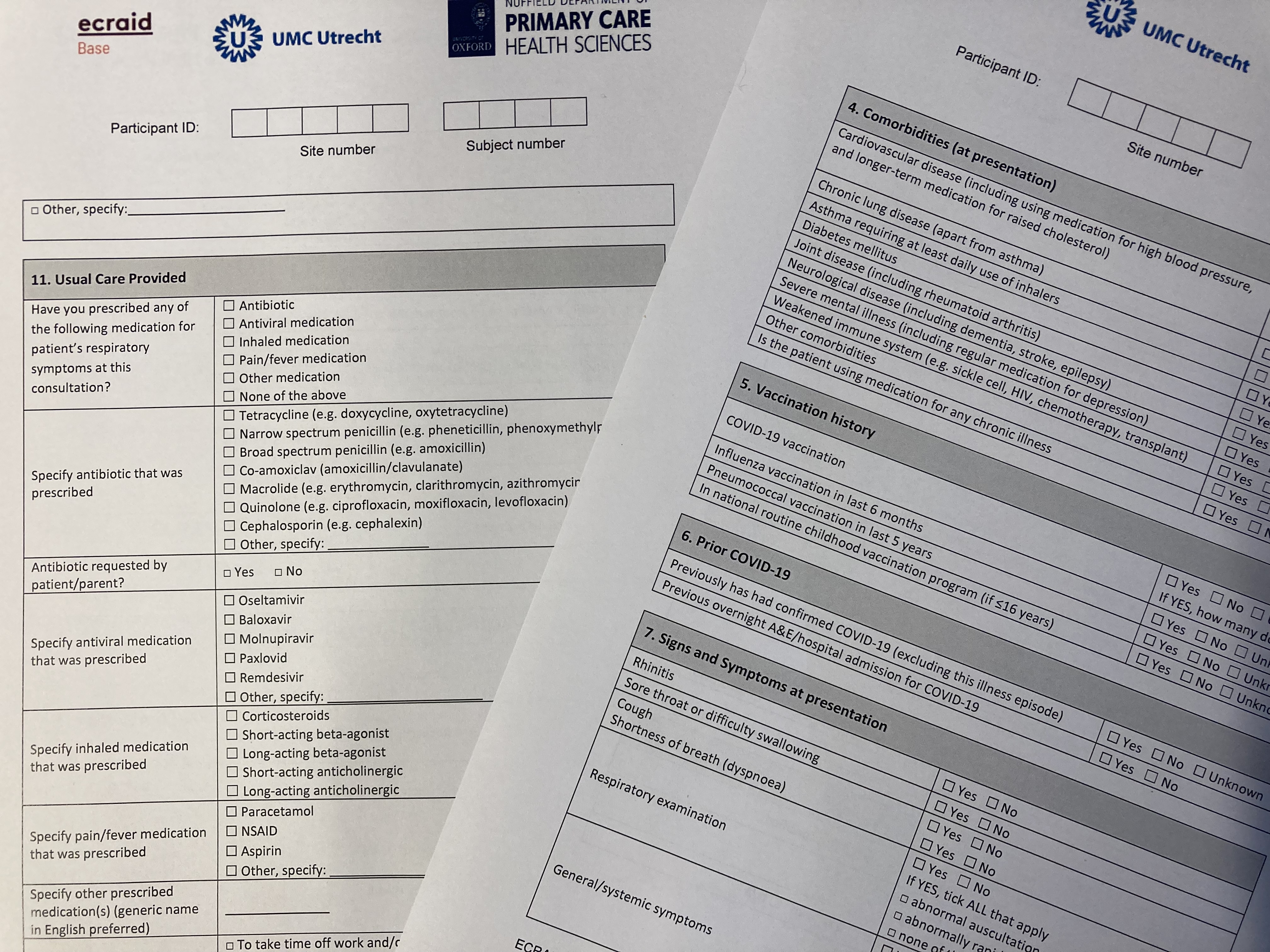
Next to antibiotics prescribing, the audit also gathers data on other prescribed medication, diagnostic testing as well as advice given to patients. The current audit is a “paper exercise” (right) with GPs recording the patients they see with respiratory tract infection symptoms in November and December. The data is then entered into an online data capture tool, either by the GPs themselves or by a member of the primary care network coordinating team in their respective countries. Read about the recent network training session for this year’s audit.
Antibiotics management
In light of World Antimicrobial Awareness Week, Alike stresses the importance of antibiotics management. “After the COVID-19 pandemic, antibiotic prescribing by GPs has increased to nearly pre-pandemic levels. With as many as 80% of all antibiotics consumed being prescribed in primary care, we must focus on reducing this amount and promote prudent prescribing to fight AMR. The knowledge from our audits can help us address the variations in general practitioners' prescription behaviours across different countries in Europe, and help us promote awareness on unwarranted variations in prescribing practice."

New audit app for infectious illnesses
As part of an ongoing commitment to clinical research and antimicrobial stewardship, Alike announces a new audit initiative. This audit will broaden its focus to include the management of all infectious illness, including urinary tract, skin and gastrointestinal infections, etc. Data for this audit will be collected through a mobile application developed by St. George’s University of London. This app is specifically designed for antimicrobial stewardship programmes in low- and middle-income countries and is currently being piloted in Europe.
Are you a general practitioner and would like to participate in our primary care network audits? Get in touch with Alike van der Velden.
List of related publications
- Disease-Specific Quality Indicators for Outpatient Antibiotic Prescribing for Respiratory Infections (ESAC Quality Indicators) Applied to Point Prevalence Audit Surveys in General Practices in 13 European Countries - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Point-of-care testing, antibiotic prescribing, and prescribing confidence for respiratory tract infections in primary care: a prospective audit in 18 European countries - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Antibiotics and uncertainty of diagnosis in viral respiratory infections: Point-prevalence survey across 15 European countries - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Point prevalence audit surveys of respiratory tract infection consultations and antibiotic prescribing in primary care before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Ireland - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Primary care for patients with respiratory tract infection before and early on in the COVID-19 pandemic: an observational study in 16 European countries - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Coming soon!